 Over half a century of scientific research has documented that 7 universal facial expressions of emotion are expressed and recognized, all around the world, regardless of race, culture, nationality, religion, gender or any other demographic variable.
Over half a century of scientific research has documented that 7 universal facial expressions of emotion are expressed and recognized, all around the world, regardless of race, culture, nationality, religion, gender or any other demographic variable.
They are: Anger, Contempt, Fear, Disgust, Happiness, Sadness and Surprise.
But what exactly are the 7 basic emotions and where do other emotions such as shame, guilt and pride fit in? Read on to learn more…
What are Basic Emotions?
Basic emotions are a class of emotion for which there is abundant research evidence for certain characteristics, including
- Universal, underlying psychological triggers or antecedents
- Unique physiological signatures
- Pan-cultural cognitive gating
- Cross-cultural feelings and experiences
- Universal nonverbal expressions in the face, voice and body.
For discussion about other ways to classify basic emotions, read this past blog. These emotions have been scientifically proven to have a certain corresponding facial expression. In fact, developing the skill of reading microexpressions can help detect aspects of these expressions that are subtle or hard to determine.
How many basic emotions are there in psychology?
What are the Seven Universal Emotions?
Research over several decades have identified 7 basic emotions. The basic emotion of “Anger” can be recognized by this picture all around the world, no matter what age, religion or gender you are, or what language you speak and it may be one of the most important in detecting threatening behavior.
Anger can be characterized by these characteristics below:

Similarly, Fear is one of the seven basic emotions. Fear is recognized all around the world by this facial expression of emotion, with the characteristics which can be seen below. Its important to note that other words describing fear are also expressed by this same face (or portions of this face). Emotions such as scared, mortified, horrified and petrified all have characteristics of this expression.

There are other basic emotions such as disgust, contempt, happiness, sadness and surprise. Their characteristics can be seen below:
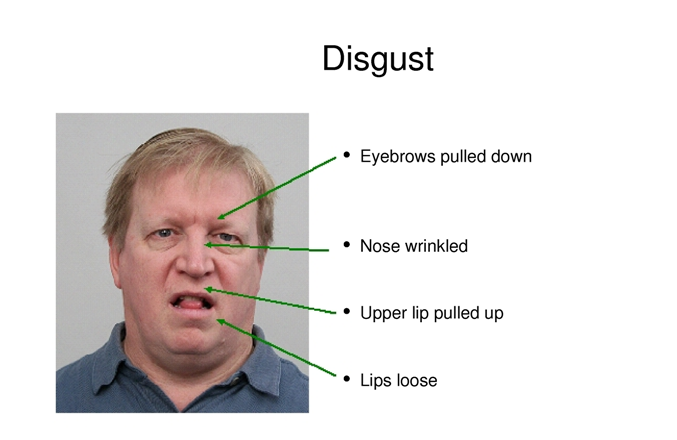

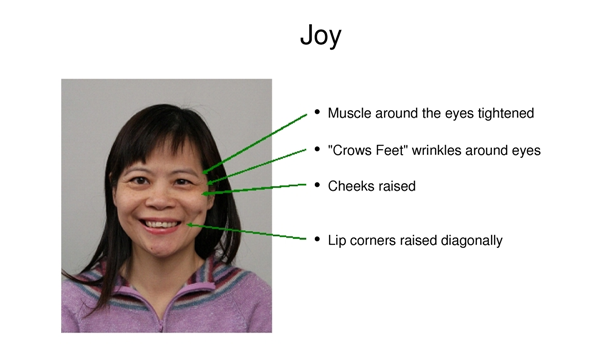


What about other Emotions?
We often get asked about emotions such as shame, pride, jealously and guilt. While these emotions are important ones, they are still not considered part of the basic emotions set.  For example, there is no scientific evidence showing that there is a universal facial expression of shame.
For example, there is no scientific evidence showing that there is a universal facial expression of shame.
However, recent research has shown there are facial and corresponding body movements that may be universal for triumph, shame, and embarrassment.
Research of the last two decades have furthered our understanding of facial expressions, emotions and nonverbal behavior.
Much of this research has linked facial expressions with other nonverbal channels – gaze, head, and whole body movements – to express emotions across cultures, such as shame and embarrassment, love, gratitude, sympathy, pride, and triumph.
Read more about our research on triumph here.
Proceed With Caution…
Be wary when you see or hear people labeling other expressions as universal emotions that are not in the basic emotion set. There is little evidence backing up their claims.
To learn the latest updates regarding The Universality of Facial Expressions of Emotion, check out the blog post below
The Universality of Facial Expressions of Emotion, An Update
*Please note that the images used in this blog post are property of Humintell. Duplicating or using these images for any purpose is strictly prohibited without written consent of Humintell.
Do not forget that all emotions, including the basic ones mentioned on this Website, cannot only been SEEN as being associated with particular facial expressions, but can also be FELT. Stated differently, a blind person would know what particular emotion(s) the speaking person was feeling at the time of the conversation. It would be interesting to observe what differences and similarities, if any, exist in conversations between a person with normal vision and a blind person with regard to emotions.
What about HORROR ???
Horror falls under the “fear” expression. As does scared, mortified, petrified, etc.
What about compassion/empathy?